Interactive Audio Visualizer
While traveling for the holidays, I found myself with spare time but only a laptop on hand. So I tried re-creating a previous experiment using portable web technologies that can run on any device with a browser, including React and THREE.js. This ended up being a fun morning project.
Click HERE for an Interactive Demo
Note: After navigating to the app with the link above, use the GUI controls in the app to select MIC input
Creating a Reactive Grid
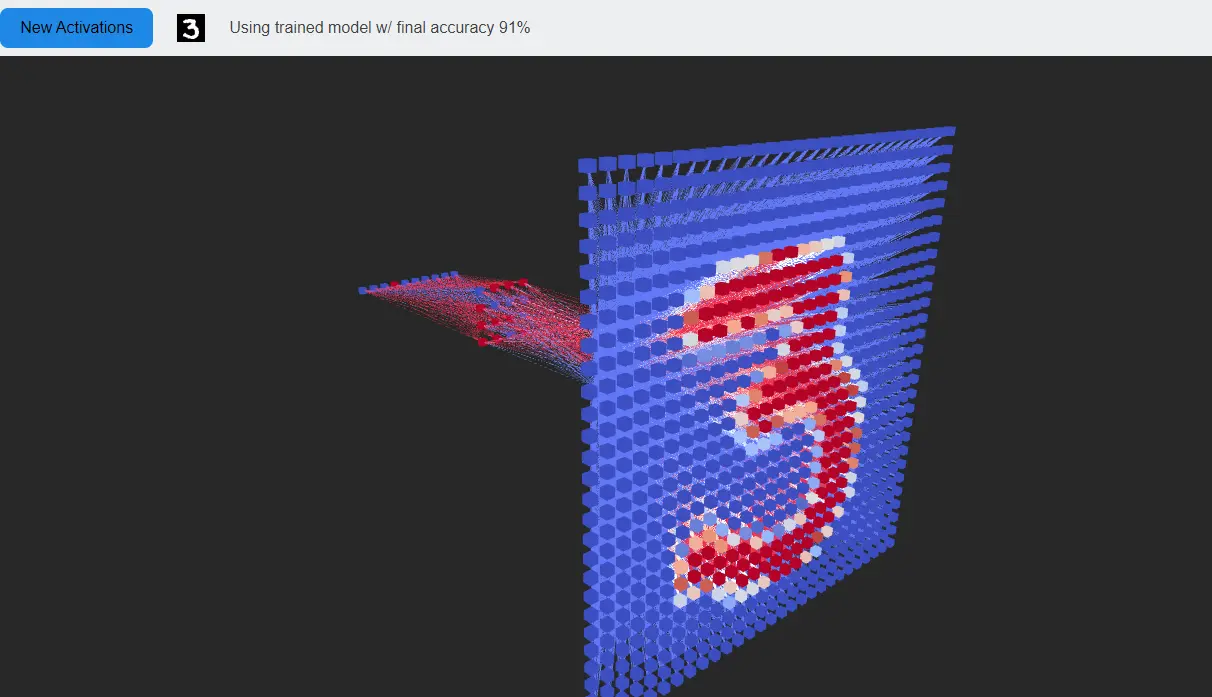
The grid is comprised of thousands of meshes. To keep things efficient, I used instanced meshes which are only created once.
<instancedMesh ref={meshRef} args={[null, null, nGridRows * nGridCols]}>
<boxGeometry attach="geometry" args={[cubeSideLength, cubeSideLength, cubeSideLength, 1]} />
<meshBasicMaterial attach="material" color={"white"} toneMapped={false} />
</instancedMesh>
The transform for each mesh is updated every frame, which is fairly lightweight operation. The meshes are indxed in row-major order.
// minimal example to set transforms on each cube in the grid
useFrame(() => {
for (let row = 0; row < nGridRows; row++) {
for (let col = 0; col < nGridCols; col++) {
let x,y,z = ...;
let instanceIdx = row * nGridCols + col;
let tmpMatrix = new Matrix4();
meshRef.current.setMatrixAt(instanceIdx, tmpMatrix.setPosition(x, y, z));
}
}
});
In reality, we want to set the transforms based on some data. To create the final animation, I apply effects to the z-offset in normalized radial coordinates measured out from the center of the grid. The following code changes z values for each cube in the grid to reflect a sin wave.
useFrame(({ clock }) => {
//in ms
const time = 1000 * clock.getElapsedTime();
const gridSizeX = nGridRows * cubeSpacingScalar * cubeSideLength;
const gridSizeY = nGridCols * cubeSpacingScalar * cubeSideLength;
const periodSec = 1 / frequencyHz;
const b = (2 * Math.PI) / periodSec;
const normQuadrantHypotenuse = Math.sqrt(
Math.pow(0.5, 2) + Math.pow(0.5, 2)
);
let phaseShift = time / 1000;
let x, y, z, idx, normGridX, normGridY, normRadialOffset;
for (let row = 0; row < nGridRows; row++) {
for (let col = 0; col < nGridCols; col++) {
idx = row * nGridCols + col;
normGridX = row / nGridRows;
normGridY = col / nGridCols;
x = gridSizeX * (normGridX - 0.5);
y = gridSizeY * (normGridY - 0.5);
normRadialOffset =
Math.sqrt(
Math.pow(normGridX - 0.5, 2) + Math.pow(normGridY - 0.5, 2)
) / normQuadrantHypotenuse;
z = amplitude * Math.sin(b * normRadialOffset + phaseShift);
ref.current.setMatrixAt(idx, tmpMatrix.setPosition(x, y, z));
}
}
// Update the instance
ref.current.instanceMatrix.needsUpdate = true;
});
Extending this idea, we can visualize arbitary data from a 1D array of values. The following code will map a referenced 1D data array into z values for each cube in the grid.
useFrame(() => {
//in ms
const gridSizeX = nGridRows * cubeSpacingScalar * cubeSideLength;
const gridSizeY = nGridCols * cubeSpacingScalar * cubeSideLength;
const normQuadrantHypotenuse = Math.hypot(0.5, 0.5);
let instanceIdx, normGridX, normGridY, x, y, z, normRadialOffset;
for (let row = 0; row < nGridRows; row++) {
for (let col = 0; col < nGridCols; col++) {
instanceIdx = row * nGridCols + col;
normGridX = row / nGridRows;
normGridY = col / nGridCols;
x = gridSizeX * (normGridX - 0.5);
y = gridSizeY * (normGridY - 0.5);
normRadialOffset = Math.hypot(normGridX - 0.5, normGridY - 0.5) / normQuadrantHypotenuse;
z = amplitude * getValueForNormalizedCoord(freqDataRef?.current, normRadialOffset);
meshRef.current.setMatrixAt(instanceIdx, tmpMatrix.setPosition(x, y, z));
}
}
// Update the instance
meshRef.current.instanceMatrix.needsUpdate = true;
});
Note the freqDataRef above. Using this reactive grid, we can reference arbitrary data to drive the animation… including audio :)
// Play some audio, assuming an audio element
// <audio ref={audioRef} crossOrigin="anonymous" />;
audioRef.current.src = "https://icecast2.ufpel.edu.br/live";
audioRef.current.play();
const updateFreqData = (instance) => {
const bars = instance.getBars();
bars.forEach(({ value }, index) => {
freqDataRef.current[index] = value[0];
});
};
analyzer = new AudioMotionAnalayzer(null, {
source: audioRef.current,
mode: 2,
useCanvas: false,
onCanvasDraw: updateFreqData,
});


Comments