Bert w/ Label Semantics
In real world applications, labeled data is often hard to come by. This makes learning based solutions difficult. If large datasets are NOT available, you have to get creative with whatever context is available. This post demonstrates a method of incorporating the semantic “meaning” of each label as a clue/prior when training few-shot systems for Named Entity Recognition. See the original paper for more details.
Most systems treat labels as arbitrary monikers. That is, models typically learn ONLY from the data’s association w/ a label and NOT directly from the label itself. Labels are often provided to a model as an arbitrary ID, integer or one-hot encoded vector. In many cases, we can do better. The natural representation of a label (written text) can carry significant meaning for the task at hand. For example, a label like “First Name” is more highly correlated w/ the word “Jonathan” than with the word “screwdriver”.
Architecture
The main idea is to use a BERT model to encode not only the input text, but also the text representation of the label itself. The inputs and labels then exist in a similar embedding space where associations should be easier for the model to learn.
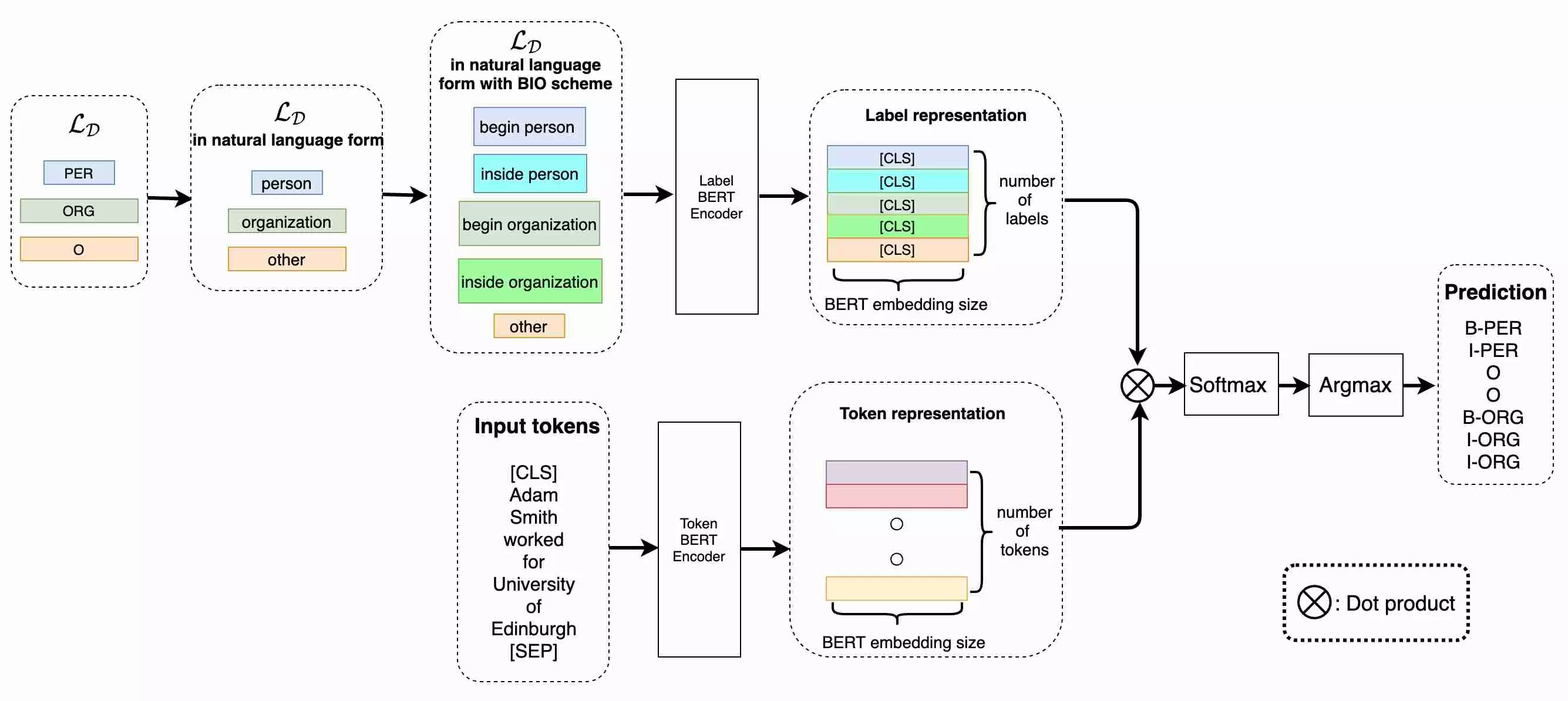
PyTorch/HuggingFace Implementation
First, some helpers to convert BIO tag labels to the “natural form” described in the paper:
def remove_prefix(s: str, pref: str) -> str:
if pref and s.startswith(pref):
return s[len(pref) :]
return s
def strip_bio_tag_prefix(bio_tag_label: str) -> str:
"""
Removes the B- or I- prefix from bio-tags
example: "B-TAG_A" ---> "TAG_A"
"""
s = bio_tag_label
for prefix in {"B-", "I-"}:
s = remove_prefix(s, pref=prefix)
s = remove_prefix(s, pref=prefix.lower())
return s
def get_natural_form_labels(id2label: Dict[int, str]) -> Dict[int, str]:
# Create natural language variants of the labels
# See paper: Label Semantics for Few Shot Named Entity Recognition
# https://aclanthology.org/2022.findings-acl.155.pdf
id2natural_form_label = {}
for idx, raw_bio_tag in id2label.items():
tag_natural_form = " ".join(
re.split(
"[^a-zA-Z0-9]+",
strip_bio_tag_prefix(bio_tag_label=raw_bio_tag).lower(),
)
)
# Retrieve the natural language version of the bio tag prefix
if raw_bio_tag.upper().startswith("B-"):
final = f"begin {tag_natural_form}"
elif raw_bio_tag.upper().startswith("I-"):
final = f"inside {tag_natural_form}"
else:
assert (
raw_bio_tag in {"other", "o", "0", "OTHER", "O"} # default "OTHER" tags
), f"Unexpected bio tag: {raw_bio_tag}"
final = "other"
id2natural_form_label[idx] = final
return id2natural_form_label
Next, an implementation of the model:
class BertWithLabelSemantics(BertPreTrainedModel):
def __init__(
self,
config: BertConfig,
tokenizer: BertTokenizerFast,
**kwargs,
) -> None:
super().__init__(config=config, **kwargs)
self.id2natural_form_label = get_natural_form_labels(
id2label=config.id2label
)
self.num_labels = len(self.id2natural_form_label)
self.token_encoder = BertModel(config=config)
self.label_encoder = BertModel(config=config)
self.tokenizer = tokenizer
self.register_buffer("label_representation", torch.zeros(self.num_labels, 768))
# Initialize weights and apply final processing
self.post_init()
def post_init(self):
super().post_init()
self.label_representation = self.compute_label_embeddings(
device=torch.device("cpu")
)
def compute_label_embeddings(
self, device: Optional[torch.device] = None
) -> torch.Tensor:
"""Computes the embedding representation of natural langauge labels
Each label is converted to natural language form, then fed as input
to a BERT encoder to yield a CLS token for the label.
returns: tensor of size (num_labels, bert_embedding_size) == (n, 768)
"""
if device is None:
device = torch.device("cpu")
labels = [
self.id2natural_form_label[idx]
for idx in sorted(self.id2natural_form_label.keys())
]
tag_max_len = max([len(l) for l in labels])
tag_embeddings = []
for label in labels:
input_ids = self.tokenizer.encode_plus(
label, return_tensors="pt", padding="max_length", max_length=tag_max_len
)
outputs = self.label_encoder(
input_ids=input_ids["input_ids"].to(device=device),
token_type_ids=input_ids["token_type_ids"].to(device=device),
attention_mask=input_ids["attention_mask"].to(device=device),
)
pooler_output = outputs.pooler_output
tag_embeddings.append(pooler_output)
label_embeddings = torch.stack(tag_embeddings, dim=0)
label_embeddings = label_embeddings.squeeze(1)
return label_embeddings
def forward(
self,
input_ids: torch.Tensor,
attention_mask: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
token_type_ids: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
labels: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
**kwargs,
) -> TokenClassifierOutput:
device = input_ids.device
if self.training:
# If training, update/re-compute label embeddings
self.label_representation = self.compute_label_embeddings(device=device)
label_representation = self.label_representation.to(device=device)
outputs = self.token_encoder(
input_ids=input_ids,
token_type_ids=token_type_ids,
attention_mask=attention_mask,
)
token_embeddings = outputs.last_hidden_state
tag_lens, hidden_size = label_representation.shape
current_batch_size = token_embeddings.shape[0]
label_embedding = label_representation.expand(
current_batch_size, tag_lens, hidden_size
)
label_embeddings = label_embedding.transpose(2, 1)
# # Batched Matrix x Batched Matrix, where batch_size == b
# A.shape == (b,m,n);
# B.shape == (b,n,k);
# torch.matmul(A,B).shape == (b,m,k);
logits = torch.matmul(token_embeddings, label_embeddings)
# So... expect logs of shape (batch_size, sequence_length, num_labels)
# Ex: (6, 512, 11)
# You can retrieve the label indices like so:
# softmax_embedding = nn.Softmax(dim=-1)(logits)
# label_indices = torch.argmax(softmax_embedding, dim=-1)
# label_indices.shape == (batch_size, sequence_length) # ex: (6, 512)
loss = None
if labels is not None:
loss_fct = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
loss = loss_fct(logits.view(-1, self.num_labels), labels.view(-1))
return TokenClassifierOutput(
loss=loss,
logits=logits,
hidden_states=outputs.hidden_states,
attentions=outputs.attentions,
)
@classmethod
def from_pretrained(
cls,
pretrained_model_name_or_path: Optional[Union[str, os.PathLike]],
config: Optional[BertConfig] = None,
**kwargs,
):
if config is None:
config = AutoConfig.from_pretrained(
pretrained_model_name_or_path,
)
for attr_name in {"num_labels", "label2id", "id2label"}:
assert hasattr(
config, attr_name
), "Config is not sufficient to load model."
assert (
0 < config.num_labels == len(config.label2id) == len(config.id2label)
), "Config is not sufficient to load model."
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(
pretrained_model_name_or_path=pretrained_model_name_or_path,
use_fast=True,
only_label_first_subword=False,
)
if not os.path.exists(pretrained_model_name_or_path):
# Assume model path is a default bert model...
# In this case, we need to instantiate a model and
# replace its encoders with pretrained bert models
model = cls(
config=config,
tokenizer=tokenizer,
)
setattr(
model,
"label_encoder",
BertModel.from_pretrained(pretrained_model_name_or_path),
)
setattr(
model,
"token_encoder",
BertModel.from_pretrained(pretrained_model_name_or_path),
)
return model
else:
return super(BertWithLabelSemantics, cls).from_pretrained(
pretrained_model_name_or_path=pretrained_model_name_or_path,
config=config,
tokenizer=tokenizer,
**kwargs,
)

Comments